Unlock the Secret World of QR Codes: The Fast and Fun Way to Connect and Engage with Customers
In 1994, Quick Response codes were developed by Japanese auto manufacturer, Denso Wave, as a way to quickly scan and track components in the manufacturing process. Fast forward to the present day and QR codes have become a game-changing tool for businesses around the world.
Here are some eye-opening facts about QR codes that you might not know:
As technology advances, it will be fascinating to see the innovative uses that QR codes will have in the future. With these codes, businesses can unlock a whole new world of interactive and engaging content that customers crave.
Up Close and Personal with QR Codes: The Origin, Creator and More
A Brief Introduction to QR Codes
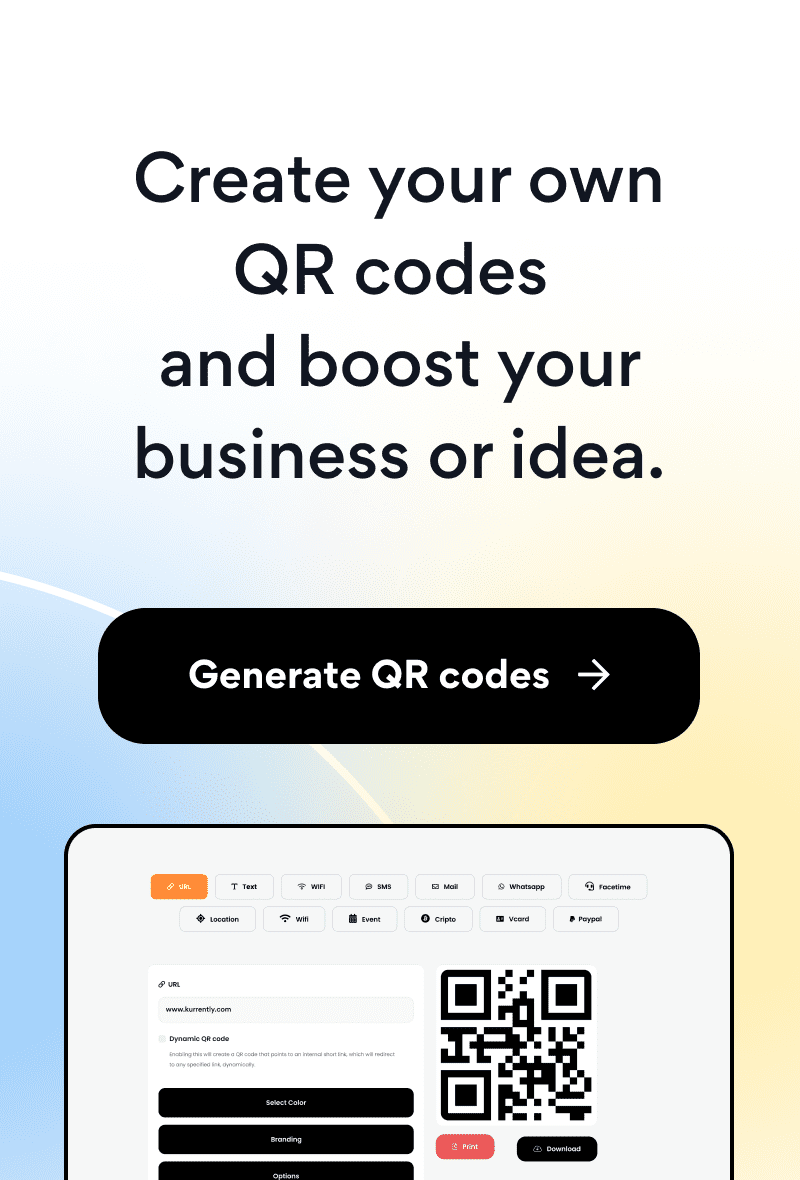
QR codes, or Quick Response codes, allow you to store more data in a smaller space than traditional barcodes, making them more versatile and practical. These two-dimensional codes are read by smartphones and other mobile devices equipped with QR scanners, and they play a significant role in digital marketing, electronic payment, inventory management systems, and more.
The History of QR Codes: Origins and Developments
QR codes date back to the late 1990s when they were invented by a Japanese corporation, Denso Wave. The company was seeking an innovative and efficient way to track car parts and components in their factories, and a typical barcode was not sufficient. A team of engineers at Denso Wave designed the QR code, a square-shaped code composed of black and white modules with a distinct pattern.
Soon after its invention, Denso Wave realized that the potential uses for QR codes extended beyond automobile manufacturing. Denso Wave released the patent for QR codes, which meant that anyone could use or modify the design for free. This move paved the way for a wide range of applications, including consumer-facing marketing campaigns, industrial automation, and logistics.
Who Created the QR Code? A Comprehensive Look
Masahiro Hara created the QR code while working at Denso Wave as a lead engineer. Hara’s background in graphic design, computer science, and data compression was instrumental in the creation of QR code. According to Hara, his inspiration for the code design came from the game of Go, where black and white stones are arranged on a board, creating different patterns.
The creation process of the QR code took around a year, and the team faced various challenges in its development. The team needed the code to be robust enough that it could be read by smartphones, even if the code was damaged or if the phone was shaking. They had to create a balance between a compact size, high capacity, and readability.
The Role of Automotive Industry in QR Code Invention
The automotive industry played a pivotal role in the invention of QR codes, as Denso Wave had initially created QR codes for the automotive industry. Car factories found the standard barcodes challenging to read due to their small size and low resolution, and the need to record more information than barcodes could hold led to the creation of QR codes.
The QR codes solved several logistical problems in the automotive manufacturing process, as they were highly readable, could hold significantly more data and took up less space compared to barcodes.
The Complex Configuration of QR Codes: How They Work
QR codes comprise a matrix of black and white squares arranged in a square grid, and they require special software to scan and read. To encode data in a QR code, a combination of encoding algorithms is employed to represent text, numeric, and other forms of data.
When a user scans the QR code with a QR code reader, the software decodes the algorithm and retrieves the stored data. QR codes can be read from any angle or orientation, making them highly versatile in their application.
Here are some exciting facts about QR codes:
- QR codes can be customized with logos and colors to create visually appealing codes for use in marketing campaigns.
- QR codes can store up to 7,089 characters of numeric data, 4,296 characters of alphanumeric data or up to 2,953 bytes of binary data.
- QR codes can link to web pages, email addresses, text messages, app downloads, image videos, and other digital media.
Thinking Beyond – The Future of QR Codes
The future of QR codes may involve incorporating more interactive elements. With advancements in technology, QR codes could become more interactive, allowing users to interact with codes in more engaging ways.
RealtyGo, a real estate company in the US, is employing QR codes in lockboxes to simplify the process of showing homes. QR codes may also be observed around museums on clothing worn by tour guides, providing interactive audio guides and additional information on the exhibits.
Advantages and Disadvantages of QR Codes in Today’s World
Advantages of QR codes:
- QR codes increase consumer engagement with brands and campaigns, resulting in deeper engagement with a product or service.
- QR codes are cost-effective and easy to design, making them suitable for small businesses to implement in their marketing campaigns.
- QR codes allow for data tracking, which helps businesses understand consumer behavior and market trends.
Disadvantages of QR codes:
- QR codes are not universally recognized and are only scannable with a smartphone equipped with a QR code reader.
- QR codes require an internet connection to access the data stored in the code, which could limit reach in areas with poor connectivity.
- QR codes are subject to fraud, as codes designed with malicious intent can redirect users to unsafe sites, access private data, and more.
In conclusion, QR codes have come a long way since their invention, becoming a valuable tool for various industries and businesses. Their versatility, speed, and compactness make them an attractive option for marketers and logistics managers alike. While QR codes have evolved and will continue to do so, the potential uses and developments of QR codes in the future are limitless.