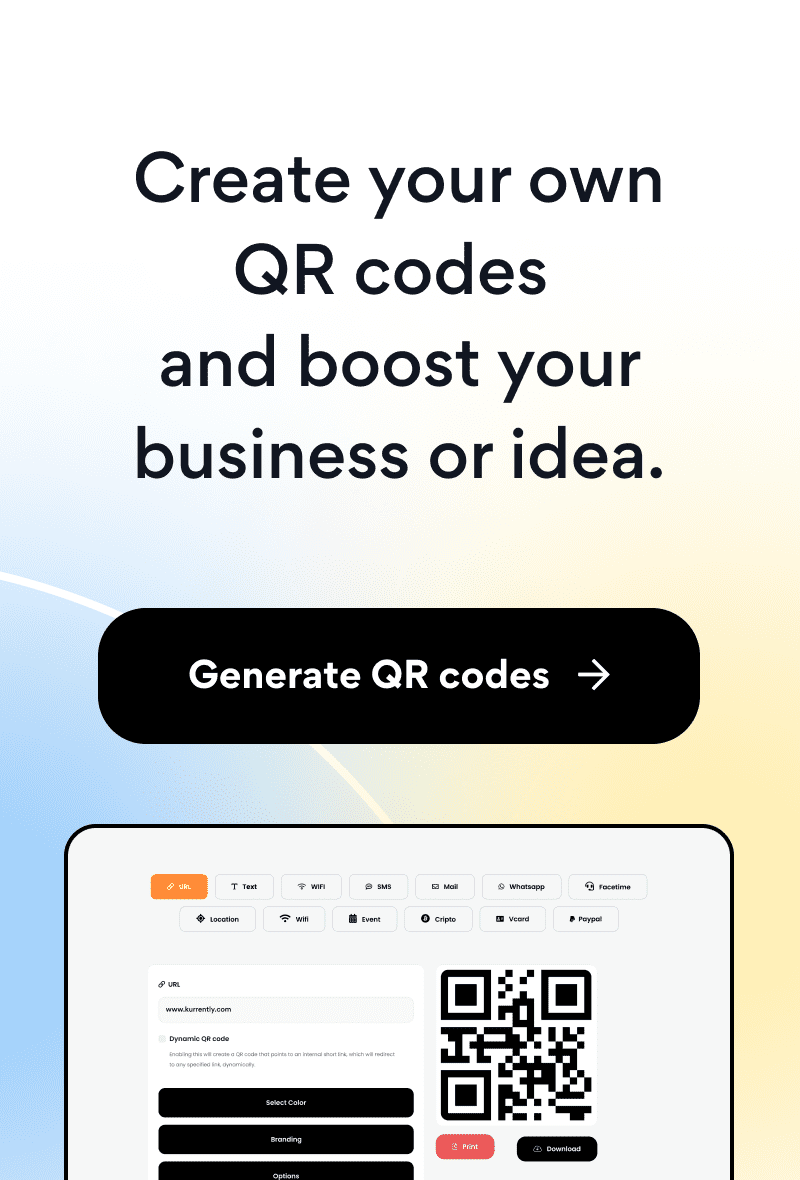
Looking to share information in a modern and speedy way? Look no further than the Quick Response code, or QR code. These two-dimensional matrix barcodes can store a range of data types, from URLs to contact information to plain text. Here’s how it works:
In short, QR codes are a quick and convenient way to share information. With error correction and encryption features, they’re also a secure choice. Give them a try today!
QR Code: A Brief Introduction
A QR code, short for Quick Response code, is a type of two-dimensional barcode that allows digital information to be easily readable by a smartphone or barcode scanner. They were first developed in 1994 by a Japanese company called Denso Wave and were primarily used in the automotive industry to track vehicles and inventory. However, in recent years, QR codes have become ubiquitous in various industries and have found numerous applications in marketing, advertising, product packaging and more.
The Anatomy of a QR Code
A QR code consists of black and white modules arranged in a square pattern on a white background. The black modules represent data, while the white modules represent the spaces around them. In the corner of the QR code, there is typically a square finder pattern that helps the scanner to locate the code. Additionally, there is typically a quiet zone around the code to reduce interference from other patterns or colors.
QR Code Encoding: How Information is Stored
QR codes are capable of storing a variety of information types, including website URLs, contact information, location data, and more. The information is encoded into the QR code using various encoding schemes, such as alphanumeric, numeric, and binary. The more information that is stored in the code, the more modules will be required and the denser the pattern will become.
It is important to note that QR code encoding can affect the readability and scannability of the code. Therefore, it is important to ensure that the code is formatted correctly and that the information is entered accurately.
QR Code Scanning: How Information is Retrieved
To scan a QR code, you need a smartphone or barcode scanner with a built-in QR code reader. When the scanner reads the code, it translates the pattern of black and white modules back into digital information that can be displayed on the device’s screen. Depending on the type of information stored in the code, the device may launch a website, display contact information, or even make a phone call.
It is important to note that QR codes should be scanned under optimal conditions, such as good lighting and a steady hand. Scanning under poor conditions can result in errors, and the code may need to be rescanned to retrieve the information.
QR Code Use Cases: Where and Why are They Used?
QR codes can be found in a variety of industries and applications. Here are some examples:
- Marketing and Advertising: QR codes are often used in print ads, billboards, and product packaging to direct customers to a website or offer.
- Event Management: QR codes can be used for event registration, ticketing, and check-in.
- Retail and Restaurants: QR codes can be used for mobile ordering, loyalty programs, and contactless payments.
- Manufacturing and Supply Chain: QR codes can be used for inventory tracking, quality control, and asset management.
It is important to note that QR codes should be used strategically and with a clear purpose. If they do not provide value to the customer or are used incorrectly, they may be ignored or even perceived as a negative experience.
The Future of QR Codes: Evolutions and Innovations
As technology continues to evolve, QR codes are also expected to evolve and innovate. Some potential advancements include:
- Dynamic QR codes that can be edited and updated in real-time
- QR codes that are capable of interactive features, such as augmented reality
- QR codes that are integrated with voice assistants and other smart devices
As QR codes continue to evolve, it is important for businesses to stay up-to-date on the latest trends and opportunities.
QR Code Best Practices: How to Create and Use Them Effectively
Here are some best practices for creating and using QR codes effectively:
- Keep the code simple and easy to read
- Make sure the code is formatted correctly and that the information is entered accurately
- Provide clear instructions on how to scan the code
- Ensure the landing page is optimized for mobile devices and provides value to the customer
- Track and analyze the performance of the QR code to measure its effectiveness
By following these best practices, businesses can create and use QR codes that provide value to their customers and help them achieve their goals.
In conclusion, QR codes have come a long way since their introduction in 1994, and they continue to find new applications and innovations. Businesses that understand how QR codes work and how to use them effectively can benefit from this versatile technology and provide value to their customers.