Unlocking the Power of QR Codes: A Simple Guide to Using Them Effectively
If you haven’t heard of QR codes, you’ve likely seen them around: those small, square-shaped digital puzzles that seem to be everywhere these days. But what exactly are they, and how do they work?
QR codes, also known as Quick Response codes, are a popular and convenient way to access information through your smartphone’s camera. They can be used for a variety of purposes, from marketing campaigns to event tickets, and their popularity continues to grow as smartphones become increasingly prevalent.
Here’s how they work:
In short, QR codes are a quick and easy way to access information without having to manually type in a web address or search for specific content. By simply scanning the code, users can access a wealth of information with ease.
With their versatility and ease of use, it’s no wonder QR codes have become such a staple of modern society. So why not give it a try and see how it can enhance the way you interact with the world?
QR Code: An Introduction
QR codes have become an increasingly popular form of barcode scanning for many businesses and individuals looking to convey information quickly and easily. The technology behind QR codes has been around for some time, but in recent years, the use of QR codes has exploded thanks to advances in smartphone technology. The ability to carry a wealth of information in a small square has made QR codes a vital tool for businesses, marketing campaigns, and the sharing of personal information more convenient.
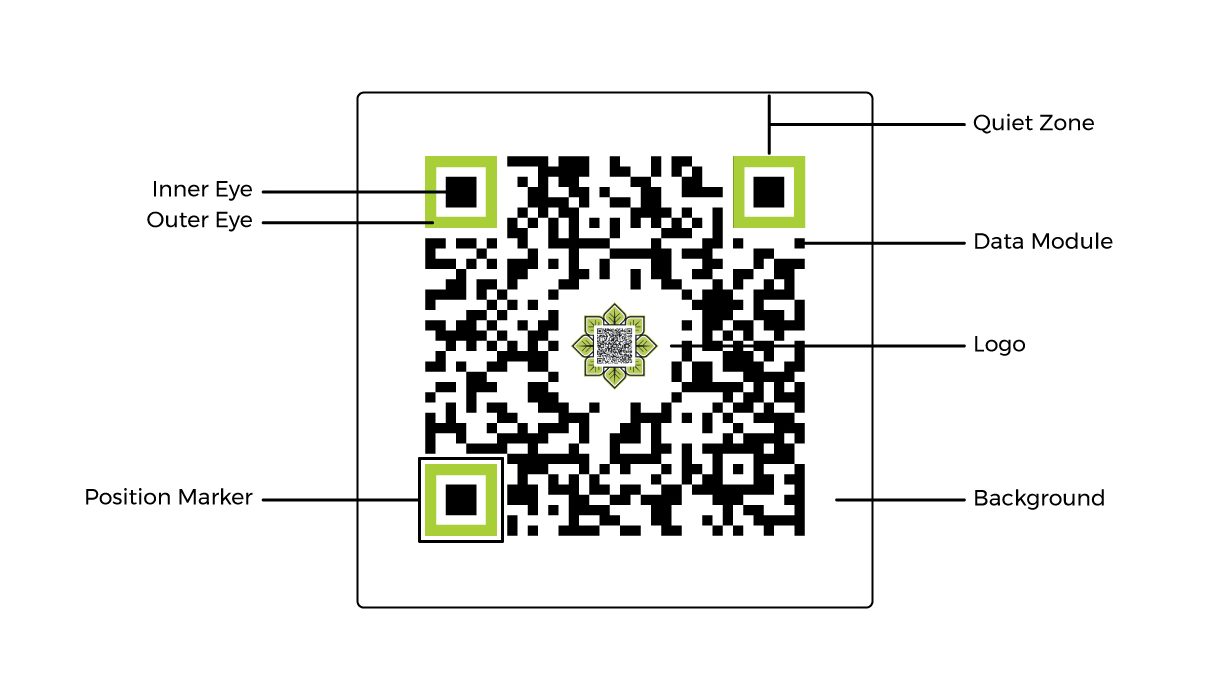
The Structure of a QR Code
QR code stands for Quick Response Code, and they are made up of a series of black and white squares arranged in a square grid pattern. The basic structure of a QR code includes four main elements: the finder pattern, the timing pattern, the alignment pattern, and the quiet zone. The finder pattern guides the scanner to the QR code, the timing pattern determines the size of the squares, and the alignment pattern helps the scanner locate the QR code correctly. The quiet zone is an area of white space around the QR code used to improve the scanability of the code.
QR Codes and Data Encoding
The information encoded in QR codes can be any type of data, from URL links to text messages, and from phone numbers to Wi-Fi logins. QR codes use several different types of data encoding, including numeric code, alphanumeric code, and binary code. Numeric code is used when the data consists of just numbers, such as a phone number or a date. Alphanumeric code can be used when the data consists of both numbers and letters, such as a website URL. Binary code is used when the data consists of a combination of two or more types of data, such as an image or video.
Key Point: One of the key advantages of QR codes is that they allow a large amount of data to be stored in a compact space.
Scanning QR Codes: The Basics
QR codes are typically scanned using a smartphone or tablet camera equipped with a QR scanner app. The scanner app reads the code, translates the data, and performs the appropriate action. In many cases, this action leads the user to a website or app. QR codes can also be scanned using dedicated QR scanners, commonly found in many stores and shops. When scanning a QR code, it’s important to ensure that the camera is focused properly and that the QR code is clean and not damaged.
Key Point: One of the key benefits of scanning QR codes is that there is no need to enter data manually.
QR Code Applications
QR codes have a wide range of applications, and they are used in many different industries, including advertising, retail, and healthcare. They can be used to link to websites, provide contact information, and even to make purchases. QR codes can also be an incredibly useful tool in the classroom, helping students to access additional resources quickly and easily. Another popular use of QR codes is in hotel rooms, where they are used to provide guests with a wealth of information about the hotel, its facilities, and its services.
Examples of QR Code Applications:
- Product Information: Scanning QR codes on products can provide customers with detailed information about the product, including nutritional information and price comparisons.
- Event Management: QR codes can be used to manage events, such as conferences and trade shows, by providing attendees with information about the schedule, the venue, and directions.
- Mobile Payments: QR codes can be used for mobile payment systems, allowing customers to pay for goods and services via their mobile device.
Understanding QR Code Error Correction
QR codes are designed to be resistant to damage, but they are not infallible. Errors can occur due to a number of factors, such as low light, poor focus, or a dirty or damaged QR code. QR codes are designed with error correction technology to help mitigate these problems. This technology allows QR codes to be read even if a small part of the code is damaged or obscured. The level of error correction can be adjusted depending on the intended use of the code.
Key Point: QR codes with higher error correction are more resistant to damage but may be larger in size.
The Future of QR Codes
As technology continues to evolve, QR codes are likely to become even more prevalent. The wide range of applications for QR codes means that new uses will continue to emerge, and businesses will continue to find innovative ways to use them. One possible future application of QR codes is as tools for augmented reality. With the rise of augmented reality technology, QR codes could be used to create interactive and immersive experiences for users.
QR Codes and Cybersecurity
As with any technology, QR codes are not immune to cyber attacks. Cybercriminals can use malicious QR codes to direct users to dangerous websites or to steal sensitive data. To protect against these attacks, users should be careful when scanning QR codes and should only scan codes from a trusted source. Businesses should be diligent in their use of QR codes, ensuring that they are secure and that they are not used to collect sensitive data from customers.
Key Point: QR codes are a valuable tool, but users must be mindful of the potential risks associated with their use.
In conclusion, QR codes are a versatile and powerful tool that enables businesses and individuals to share information quickly and efficiently. From advertising to education to mobile payments, the wide range of applications for QR codes means that their use is likely to continue to grow in the coming years. Understanding the structure of QR codes, as well as data encoding, error correction, and cybersecurity risks, is essential in using them efficiently and safely.