Have you ever noticed those black and white square codes on posters and products? They are called QR codes, and they have become increasingly useful for COVID-19 related purposes. Let’s dive into how QR codes work for COVID:
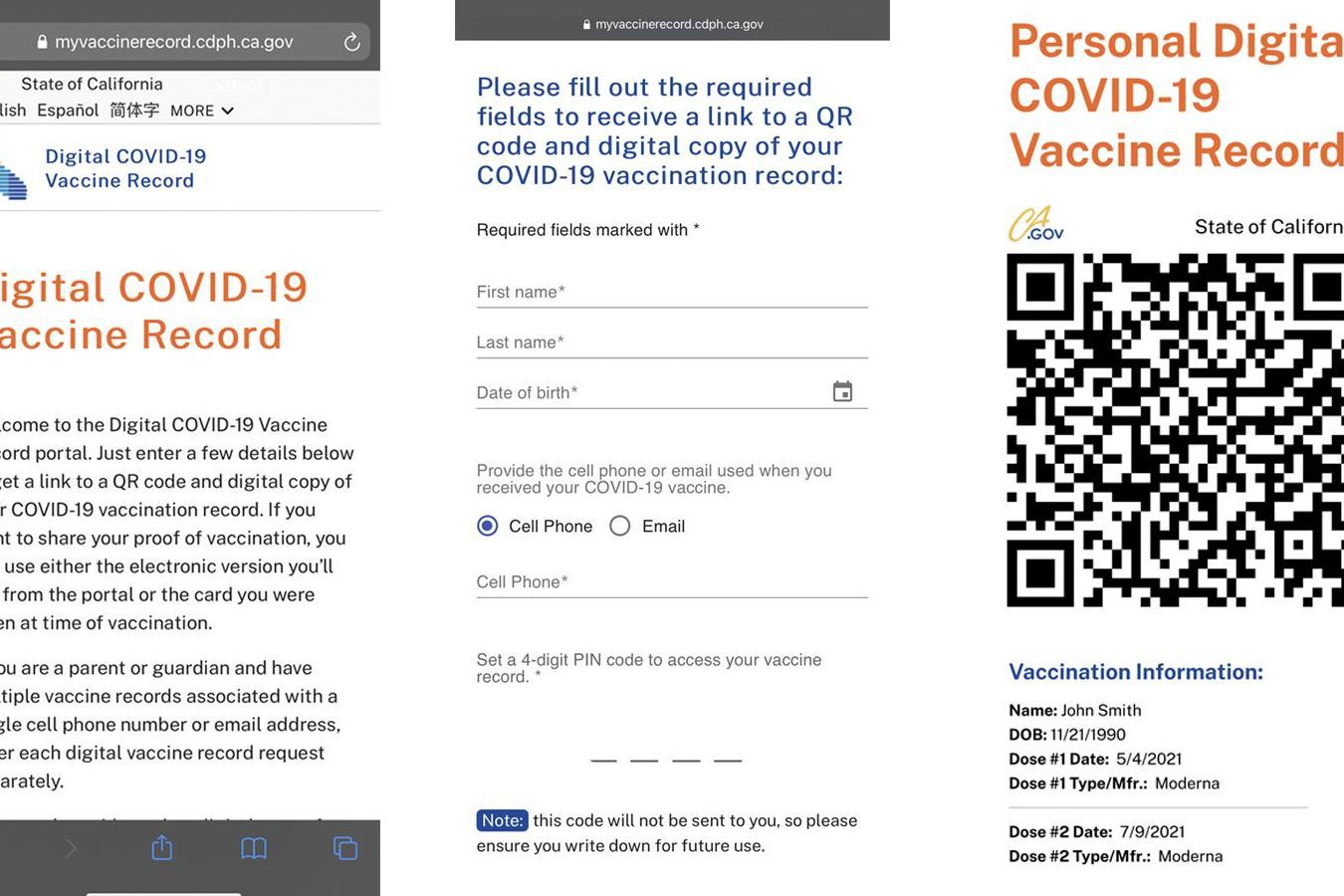
QR code as a digital COVID certificate: Say goodbye to rummaging through papers for your COVID certificate. QR codes hold all the information you need, from your name to your vaccination status.
Electronic signature for authenticity verification: QR codes have an electronic signature that confirms their authenticity. No more worries about tampered certificates.
Verification made simple with scanning: With just one scan of your phone, you can prove your COVID status at workplaces, schools, and even public transport.
Tracking and tracing made easier: QR codes help in tracking and tracing COVID cases. The data collected can be used to determine the spread of the virus and help control it.
QR codes have made the verification and tracking of COVID-19 certificates a breeze. Their implementation has played a significant role in containing and fighting the pandemic.
How does QR code work for COVID?
Introducing QR Codes for COVID Certificates
As the world continues to grapple with the COVID-19 pandemic, many countries have implemented measures to curb the spread of the virus. One of these measures is the use of COVID certificates. A COVID certificate is a document that confirms an individual’s COVID-19 vaccination status, test results or recovery status. To help manage the COVID certificates, many countries have introduced QR codes for COVID certificates. The QR codes are designed to help make the verification process easier.
The Advantages of QR Codes for COVID
QR codes come with several advantages for COVID certificates. Firstly, they are more convenient than traditional paper formats. Instead of carrying around a bunch of papers, individuals can simply scan their QR codes. Secondly, QR codes can help reduce the risk of fraud. QR codes contain an electronic signature that can verify whether the certificate is genuine or not. This means that individuals cannot simply create fake certificates with the use of QR codes. Lastly, using QR codes can make the verification process faster and more efficient. Instead of manually checking documents, health officials can scan the QR codes and immediately verify an individual’s COVID certificate.
Understanding the Formation of QR Codes
QR codes are essentially two-dimensional barcodes that can store a large amount of information. The information is encoded into a grid of black and white squares. The QR code contains a URL that leads to a destination site containing the vaccine, test, or recognition details. The structure of the QR code allows for its immediate recognition by smartphones and other reading devices. The reading device extracts the encoded information and displays it in a user-friendly format.
Below are some key points about how QR codes are constructed:
- A QR code consists of a square matrix of black and white squares.
- A QR code can store a large amount of data compared to traditional barcodes.
- Information is encoded as a series of bits, which is then converted into a matrix of black and white squares using a specified algorithm.
- The QR code contains a finder pattern that helps to locate the code, an alignment pattern to correct for distortions, a timing pattern to permit quick scanning, and other control data.
Verification of Authenticity of COVID Certificates
The authenticity of COVID certificates is validated through the use of electronic signatures. An electronic signature is a sequence of characters that identifies the entity that signed the document or message and often indicates the signer’s intent. Unlike traditional signatures, electronic signatures cannot be forged, making them more secure. The QR code on a COVID certificate contains an electronic signature to certify its authenticity. When scanned, the signature is verified by a public key certificate authority before the certificate is deemed genuine or otherwise. This helps to reduce the incidence of fraudulent certificates.
Step-by-Step Guide to Scanning QR Codes for COVID
Below is a step-by-step guide to scanning QR codes for COVID certificates:
- Unlock your smartphone and open your camera app on iPhones or Google Lens on Android.
- Point the camera at the QR code. The camera recognizes the code and should display a notification, asking you to click a link.
- Click the notification link to access the data contained in the QR code.
- The link should take you to a website that displays all the information contained in the QR code. You can verify the information, and it’s authenticity.
The Future of QR Codes in COVID Certification
QR codes have demonstrated their efficacy in the management of COVID certificates. It is likely that their use will become more widespread in the coming years, as governments continue to introduce measures to stop the spread of the virus. As a result, QR codes are likely to play an increasing role in the management of health certificates in general. Moreover, as technology advances, QR codes are likely to become even more efficient, reliable and secure.
In conclusion, QR codes for COVID certificates represent an innovative and convenient way to manage the spread of the virus. They offer several advantages over traditional paper formats, including increased security and efficiency. By using electronic signatures to verify the authenticity of certificates, QR codes help reduce the risk of fraud. In the long term, QR codes are likely to become increasingly important in the management of health certificates.